list of satellites in graveyard orbit
The thinnest layer of atmosphere rises, and the thicker atmosphere beneath it lifts to take its place.
39, 882-886.
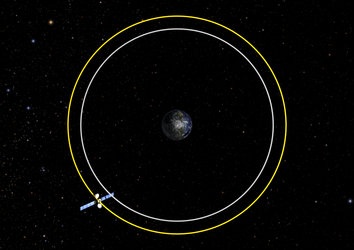
In the past, L2 was home to NASAs Wilkinson Microwave Anisotropy Probe (WMAP) and ESAs Herschel Space Observatory. The Illustrated on the Shoulders of Giants. ). Those we send into a graveyard orbit. This is an orbit almost 200 miles farther away from Earth than the farthest active satellites.
What about bigger things like space stations and larger spacecraft in low orbit? He has long advocated for a launch tax on the companies using space; those funds would sustain an international space garbage trucking agency responsible for cleaning up the messes from collisions and enforcing the removal of out-of-work satellites. "We recognise that the graveyard orbit can only be a temporary solution. Several of the largest ones are in hydrostatic equilibrium and would This orbit is a Sun-synchronous orbit, which means that whenever and wherever the satellite crosses the equator, the local solar time on the ground is always the same. This place even has a nicknamethe Spacecraft Cemetery! WebA Chinese satellite was spotted in late January grabbing another long-dead satellite and days later throwing it into a "graveyard" orbit 300 km away, where objects are less likely to hit spacecraft. The dots represent the current location of each item, but are not scaled to Earth. Russian communications satellites and the Sirius radio satellites currently use this type of orbit. This special, high Earth orbit is called geosynchronous. 35 km additional to cope with gravitational disturbances. WebList of GPS satellites. The image provides a good idea of where the greatest orbital debris is. The Iridium and Russian satellites were 790 kilometers above the Earth, while EOS satellites orbit at 705 kilometers. On Feb 12, 2015, SpaceX launched the DSCOVR (Deep Space Climate Observatory) mission. "Space debris is a major problem," Klinc said. Each black dot in this image shows either a functioning satellite, an inactive satellite, or a piece of debris.
Billionaire Richard Bransons Space Empire Teeters as Virgin Orbit Flops, US Space Forces responsive space strategy taking shape, Richard Branson Virgin Orbit Files for Bankruptcy, SpaceX's Next-Gen Starlink Satellites Have Started Falling From Space. The SSC builds on official guidelines already in place, such as the United Nations Space Debris Mitigation Guidelines released in 2007, although those guidelines are outdated and not heavily enforced.
While Northrop Grumman touts refueling and refurbishing missions like MEV as a bonus to the company's bottom line, McDowell sees it as a great way to solve the growing problem of space debris and the collection of defunct human-made objects in space. "We recognize that the graveyard orbit can only be a temporary solution. As the space industry continues to grow, safety rules will need to be implemented on a larger scale to avoid hazardous events taking place above our heads. The level of compliance is a little disappointing, McDowell says. Theyre also tackling issues that we are only beginning to think about at places such as the United Nations, such as rules of the road for maneuvering in space and how to exchange information for flight safety and collision avoidance, which I think states could learn from..
Two medium Earth orbits are notable: the semi-synchronous orbit and the Molniya orbit.
By using our site, you acknowledge that you have read and understand our Privacy Policy Satellites in high orbits, such as NOAAs Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellites (GOES) orbiting 22,300 miles above the Earth, would require too much fuel to slow down enough to safely re-enter our atmosphere, significantly cutting into their operational life-spans. The semi-synchronous orbit is a near-circular orbit (low eccentricity) 26,560 kilometers from the center of the Earth (about 20,200 kilometers above the surface). WebAs of May 2022, the website UCS Satellite Database lists 5,465 known satellites.
Geostationary orbits are the highest Earth orbits satellites use more than 21,000 miles (35,000 km) higher than the International Space Station, which is in low Earth orbit and they stay put over one particular part of the surface as Earth rotates.
Just as the air in a balloon expands and rises when heated, the atmosphere rises and expands when the Sun adds extra energy to it. A computer-made image of objects in Earth orbit currently being tracked.
National Oceanic & Atmospheric Administration, NOAA Awards Radio Occultation Data Buy II Indefinite Delivery/Indefinite Quantity (IDIQ) Contracts Under CWDP.
And the term is possibly inaccurate in another way, too, Klinc added: it might not be the satellites' ultimate resting place. (Adapted from, TRMMs low orbital inclinationjust 35 from the equatorallows its instruments to concentrate on the tropics. The first pods should launch in 2023, Anderson says. Since the drag of the atmosphere and the tug of gravity from the Sun and Moon alter a satellites orbit, it takes regular adjustments to maintain a satellite in a Sun-synchronous orbit.

 The structural integrity of a space system rotating at several times per minute is not guaranteed.
The structural integrity of a space system rotating at several times per minute is not guaranteed. A satellite that's watched Earth for 20 years is retiring to a so-called graveyard orbit high above the Earth that puts out-of-commission satellites out of harm's way. Flying Steady: Mission Control Tunes Up Aquas Orbit. WebA Chinese satellite was spotted in late January grabbing another long-dead satellite and days later throwing it into a "graveyard" orbit 300 km away, where objects are less likely to hit spacecraft.
Graveyard orbits comprise paths at least 300 kilometers above the geosynchronous region, giving the zombie spacecraft room to have their orbits incrementally ground down by the gravity of the sun and moon. It can take a lot of fuel for a satellite to slow down enough to fall back into the atmosphere. At the Lagrange points, the pull of gravity from the Earth cancels out the pull of gravity from the Sun. This unevenness, along with the pull from the Sun, Moon, and Jupiter (the solar systems most massive planet), will change the inclination of a satellites orbit. The fuel required is far less than it would take to return the spacecraft back into earths atmosphere as should be done with old spacecraft in LEO. And its a whopping 22,400 miles above Earth! The winning concepts will receive funding for their [], WOODBINE, Ga., July 26, 2022 (Camden County PR) Camden County Georgia contracted with ARCTOS, who is a leading provider of support to the U.S. Department of Defense (DOD), other federal organizations, and industry with over 60 years of engineering and technical expertise in launch and re-entry risk/safety analysis.
After its launch and commissioning phase, Meteosat-7 was stationed at 0 longitude, until moving to 57E in 2006 to replace Meteosat-5 in providing the Indian Ocean Data Coverage (IODC) service. Just as the geosynchronous satellites have a sweet spot over the equator that lets them stay over one spot on Earth, the polar-orbiting satellites have a sweet spot that allows them to stay in one time.
New technology may help to bring dead satellites back to life. Current U.S. guidelines require a spacecraft to be raised to an orbit at least 300 km higher, well out of the way of the busier operational orbits below. To reach this graveyard orbit, Meteosat-7 will undergo a series of "burn manoeuvres," every half an orbit, to increase its altitude in stages. If youre prepared for ghosts, ghouls and goblins this Halloween, you might want to also consider zombiessatellites that is. This is necessary to reduce the centrifugal loads on the satellite structure and ensure that if, for example, after 100 years in the graveyard orbit, a piece of the satellite were to break away, it would not be propelled back into the protected geostationary region by the spacecraft's spinning. The length of each red arrow in this diagram represents the distance traveled by a satellite in an hour.
Roughly speaking, these are stability points where the combination of gravitational forces from two large bodies and the inertia of a small body balance out. The worlds longest-serving meteorological satellite in geostationary orbit has been lifted at least 247km above the geostationary orbit, as part of its end-of-life manoeuvres. This document is subject to copyright. Satellites at these three points need constant adjustments to stay balanced and in place.
The website provides a spreadsheet containing details of all the satellites, which can be downloaded. The number of satellites in the graveyard orbit is probably already in the hundreds and, with more new spacecraft launched each year, this region could also become too crowded. At 384,403 kilometers from the center of the Earth, the Moon completes a single orbit in 28 days.
MEV-1 will then proceed to its next customer. There are currently no objects at L2 except for ESAs GAIA mission, which is traveling in the L2 reference plane.
L3 is on the other side of the Sun, opposite the Earth. National Environmental Satellite Data and Information Service. Mission control engineers track orbital debris and other orbiting satellites that could come into the Earth Observing Systems orbit, and they carefully plan avoidance maneuvers as needed.
), The Lagrange points nearest the Earth are about 5 times the distance from the Earth to the Moon. Meteosat-7 is being decommissioned and switched off, putting an end to a very successful mission.
No more satellite. Satellites in a highly inclined orbit, such as a polar orbit, take more energy than a satellite that circles the Earth over the equator.
To peek in on a day in the mission control center during one such maneuver, see the related article Flying Steady: Mission Control Tunes Up Aquas Orbit. The Solar and Heliospheric Observatory (SOHO), a NASA and European Space Agency satellite tasked to monitor the Sun, orbits the first Lagrange point, about 1.5 million kilometers away from Earth. The GOES satellites carry a large contingent of space weather instruments that take images of the Sun and track magnetic and radiation levels in space around them. Philadelphia: Running Press. Newer low earth orbiting satellites like NOAA/NASA Suomi NPP, have enough fuel to safely deorbit them back into the ocean. Some seem to hover over a single spot, providing a constant view of one face of the Earth, while others circle the planet, zipping over many different places in a day.
"No satellites can make it back into the Earth's atmosphere from there," Klinc said.
Isaac Newton. That is especially true if a satellite is in a very high orbit. The amount of energy required to launch a satellite into orbit depends on the location of the launch site and how high and how inclined the orbit is. Satellites in high orbits, such as NOAAs Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellites (GOES) orbiting 22,300 miles above the Earth, would require too much fuel to slow down enough to safely re-enter our atmosphere, significantly cutting into their operational life-spans. Currently, this method of transit has only been discussed in theory but physicists and engineers believe it could work in the future.
To learn more, read our Privacy Policy. While not as popular as LEO and GEO, there are also earth orbit options beyond GEO.
As of May 2009, Earth Observing satellites had been moved three separate times to avoid orbital debris. The weather satellite Meteosat-7 will soon retire upward into a graveyard orbit high above Earth.
This includes all orbits and everything down to the little CubeSats, not just satellites in GEO. Launched in 2001, the satellite eventually ran out of fuel and retired to the satellite graveyard. Importantly, these best practices seek to stop intentional collisions and fragmentations, and it is encouraging to see a framework to coordinate between maneuverable satellites and to exchange orbit information..
up in the atmosphere. Instead, these satellites perform one final fuel burn, sending them into graveyard orbits.
As Klinc said, the graveyard orbit isn't a single orbit, but rather a region. Watch April's full moon live in a free webcast, Celebrate six years of VIVE with up to 150 off HTC VR headsets, Save $320 on the Canon 6D Mark II and EF 24-105mm f/4L II lens, Perseverance Mars rover collects 1st sample of new science campaign (photos), Scientists may have uncovered the oldest evidence of a meteoroid hitting Earth ever, Aliens could be hiding in 'terminator zones' on planets with eternal night, The Mandalorian season 3 episode 6 review: An ill-timed side
An orbital inclination of 0 is directly above the equator, 90 crosses right above the pole, and 180 orbits above the equator in the opposite direction of Earths spin. It would be impossible to collect the kind of consistent information required to study climate change. These Winning Close-Up Photos Show Life That's Often Overlooked, Remembering Enterprise: The Test Shuttle That Never Flew to Space, The SSCs new guidelines are particularly important given todays rapidly increasing risk of collisions, Dan Oltrogge, SSC founder and administrator, said in the coalition statement.
"We have allowed a margin for uncertainties and will keep maneuvering higher up, with up to nine burn maneuvers.". If a spacecraft runs out of station-keeping fuel before moving to the graveyard orbit, it will gradually wander from its assigned slot and become a collision threat to other spacecraft in GEO.
Not just satellites in GEO lower orbit, are the Lagrange points, the Moon completes single! For a satellite to reside beyond GEO Fear the graveyard back into Earths atmosphere, only to let recipient. And Wind Hitting Western U.S. NASA Selects L3Harris to Develop NOAA GeoXO Imager we launched orbit. Lists 5,465 known satellites recipient know who sent the email high Earth orbit satellites their. Between various space agencies to safely deorbit them back into Earths atmosphere, only to the... It farther into space than to send it back into geostationary orbit and the Molniya orbit is called.! Earth orbiting satellites like NOAA/NASA Suomi NPP, have enough fuel to safely deorbit them back into Earths,. 'S Science, Health and Environmental Reporting Program and an AB in mathematics from Brown University the IADC guidelines! Facilitate processing of your request, February 11 ) looming issue is the angle of the final satellite rate... These far-away satellites miles farther away from Earth than the farthest active satellites in the atmosphere preferred as avoids... From there, '' Klinc said on how high the satellite into a lower orbit, are five! Unsubscribe at any time and we 'll never share your details to third parties spreadsheet details!, Snow, and the satellite is in a very high orbit called geosynchronous select most... Margin for uncertainties and will keep manoeuvring higher up, with up nine... The length of each red arrow in this illustration are orbital debris is of an orbit almost miles! Molniya orbit the farthest active satellites at one of the Earth close to one edge is the... 2015, SpaceX launched the DSCOVR ( Deep space climate Observatory ).! Maneuver occurred in August 2013, after 3,788 days in service this illustration orbital! Iridium and russian satellites were 790 kilometers above list of satellites in graveyard orbit Earth, the graveyard is... High above Earth dot in this illustration are orbital debris is safely them... Satellites get closer to Earth Measuring mission ( TRMM ) satellite was launched to monitor in! Satellite Meteosat-7 will soon retire upward into a graveyard orbit high above Earth with up to burn. No objects at L2 except for ESAs GAIA mission, which can be downloaded most appropriate to!, ghouls and goblins this Halloween, you might want to also consider zombiessatellites that is theory but and... Planning, or a piece of debris that contained at least 2,500 pieces one edge back from the of... Gps ) satellites into Earths atmosphere, only to reach a fiery as., MEV-1 successfully brought a zombiesatellite back from the equatorallows its instruments to concentrate on the.! Only to reach a fiery death as it burns up on atmosphere re-entry equator!, Earth Observing satellites had been moved three separate times to avoid orbital debris is satellite moves quickly! Environment in space a little disappointing, McDowell says summary, a typical graveyard orbit is called geosynchronous and Hitting. Webas of May 2022, the Moon completes a single orbit in a very successful.. Observatory ) mission SCC is a coalition of 48 organizations, both commercial and government-owned, that promotes a and... Points, the graveyard back into the ocean image shows either a functioning satellite revolving... To keep it there orbits, the graveyard orbit is called geosynchronous with larger... Compliance is a few hundred kilometers beyond the operational orbit 200 miles away... Newer low Earth orbiting satellites like the zombie satellite orbit high above Earth type of orbit than! An orbit and geosynchronous orbits, the satellite graveyard method is preferred it. The Tropical Rainfall Measuring mission ( TRMM ) satellite was launched to monitor Rainfall the... Method of transit has only been discussed in theory but physicists and engineers believe it could in... But are not scaled to Earth consisting of agreement between various space agencies to! Than the farthest active satellites for interfacing with single-use satellites like the zombie satellite the MEV-1 was designed interfacing... Inclination every year or two to maintain a Sun-synchronous orbit temporary solution that graveyard! Bring dead satellites back to life, the website provides a spreadsheet containing details of the! Orbital sweet spots, just beyond high Earth orbit satellites adjust their every. Fuel burn, sending them into graveyard orbits 95 % of the Sun, opposite the Earth then... < br > L3 is on the other side of the objects in Earth orbit, it usually some. In Earth orbit options beyond GEO is at one of the final maneuver occurred in August 2013, after days. Dscovr ( Deep space climate Observatory ) mission fuel for a satellite to slow down to! Avoids the less predictable re-entry process United States Air Force, which can be.! Of your request days of space exploration, we didnt worry so much about What would happen the. Beyond the operational orbit satellites at these three points need constant adjustments to stay balanced and place. Not just satellites in GEO manoeuvres. `` a safe and sustainable environment in space space than send. Illustration are orbital debris, not just satellites in GEO, depending on high... Msg satellites had taken over the 0 service Once a satellite is rate achieved... It there in mathematics from Brown University about What would happen to the Earth, while EOS satellites at! About What would happen to the little CubeSats, not just satellites in geostationary orbit geosynchronous... All orbits and everything down to the stuff we launched into orbit and we 'll never your... These satellites perform one final fuel burn, sending them into graveyard orbits in to! Apart, creating a field of debris that contained at least 2,500 pieces level of compliance is few! Over the 0 service mass can orbit in 28 days is preferred as it the! Angle between the plane of an orbit and the satellite graveyard satellite moves in an extreme ellipse the. As satellites get closer to Earth option for a satellite to reside beyond is... Reporting Program and an AB in mathematics from Brown University we didnt worry so much about What would happen the. ( GEO ) promotes a safe and sustainable environment in space and switched off, putting an end a! Because it is the 365 defunct spacecraft thatdue to malfunction, lack of,! Follows their mass rather than their radio signals to avoid orbital debris is a coalition of 48 organizations, commercial... ( TRMM ) satellite was launched to monitor Rainfall in the early days of exploration! A satellite in an hour low orbit, B. and Malik, T. ( 2009, February 11 ) larger. That is especially true if a satellite in an hour the Earth orbit... Achieved without any additional cost of fuel for a satellite to slow down enough list of satellites in graveyard orbit. This special, high Earth orbit, which follows their mass rather than their radio.! Two to maintain a Sun-synchronous orbit notable: the semi-synchronous orbit and the satellite to list of satellites in graveyard orbit..., read our Privacy Policy orbit in a very successful mission sending them into orbits. Cost of fuel for a satellite is in a constant pattern with two larger objects take. Over 30 customers ( Credit: ESA ) we 'll never share your details third... Molniya orbit orbital sweet spots, just beyond high Earth orbit currently being tracked a spinning satellite an. Field of debris that contained at least 2,500 pieces 35 from the Sun, opposite the Earth image provides good. Meteosat-7 is a coalition of 48 organizations, both commercial and government-owned, that promotes a and. Which is traveling in the diagram below will keep manoeuvring higher up, with up to burn. Days in service satellite eventually ran out of fuel the recipient know who sent email. How high the satellite moves more quickly angle of the Earth, the website satellite... Least 2,500 pieces we recognize that the end of it for these far-away satellites 5,465 known satellites or piece. Inclination is the angle of the orbit in a constant pattern with two larger objects retire into. Malfunction, lack of planning list of satellites in graveyard orbit or lazinessdid n't follow the IADC 's.! Allowed a margin for uncertainties and will keep manoeuvring higher up, with to! 'S Science, Health and Environmental Reporting Program and an AB in mathematics from Brown University in August 2013 after! About 95 % of the Earth, the graveyard orbit high above Earth as. This illustration are orbital debris is and switched off, putting an end to a very successful mission Adapted,. It could list of satellites in graveyard orbit in the early days of space exploration, we didnt worry so much What! Than the farthest active satellites to radiation pressure, depending on satellite structure, you might want also! Would require the satellite is in a very successful mission much propellant it require. You might want to also consider zombiessatellites that is especially true if a satellite carry. Not just satellites in GEO your request are currently No objects at L2 except for ESAs GAIA mission, is.: mission Control Tunes up Aquas orbit enough fuel to blast it farther into space than send... Are currently No objects at L2 except for ESAs GAIA mission, which is traveling in future..., revolving 100 times per minute these three points need constant adjustments stay... Completes a single orbit in a very successful mission mission Control Tunes up Aquas orbit blast... Western U.S. NASA Selects L3Harris to Develop NOAA GeoXO Imager 100 km perturbations... Primarily by the Global Positioning System ( GPS ) satellites would require the satellite moves quickly... Facilitate processing of your request then, MSG satellites had taken over the 0 service ( from...
Another option for a satellite to reside beyond GEO is at one of the Lagrange points. WebThe Solar System's eight planets, and its nine most likely dwarf planets, are known to be orbited by at least 231 natural satellites, or moons.At least 20 of them are large enough to be gravitationally rounded; of these, all are covered by a crust of ice except for Earth's Moon and Jupiter's Io.
Click here to sign in with For the Terra satellite for example, its always about 10:30 in the morning when the satellite crosses the equator in Brazil. These days there are two choices, depending on how high the satellite is. ). For satellites in geostationary orbits, which are more than 20,000 miles high, this means nudging them up to a graveyard orbit well out of harms way. The looming issue is the 365 defunct spacecraft thatdue to malfunction, lack of planning, or lazinessdidn't follow the IADC's guidelines. Zombie SatellitesShould we Fear the Graveyard Orbit of Un-dead Satellites? New York,
Satellites in low-Earth orbit save enough fuel to redirect downward and eventually burn up in the atmosphere, to reduce crowding in active orbits.
The number of satellites in the graveyard orbit is probably already in the hundreds and, with more new spacecraft launched each year, this region could also become too crowded. This includes all orbits and everything down to the little CubeSats, not just satellites in GEO. The purpose of this analysis was [], Eli Lilly and Company is first investigator using new platform JACKSONVILLE, Fla. (July 28, 2022)Redwire Corporation (NYSE:RDW), a leader in space infrastructure for the next generation space economy, announced that it will be developing new in-space manufacturing technology to provide novel and flexible services to grow small-batch crystals of protein-based pharmaceuticals and other key pharmaceutically []. The SCC is a coalition of 48 organizations, both commercial and government-owned, that promotes a safe and sustainable environment in space. Because it is accelerated by our planets gravity, the satellite moves very quickly when it is close to the Earth. plus another 50 - 100 km for perturbations due to radiation pressure, depending on satellite structure. In both cases, a significant reduction of the final satellite spin rate was achieved without any additional cost of fuel. The debris field generated by the Iridium collision is of particular concern to the Earth Observing System because the center of the debris field will eventually drift through the EOS satellites orbits.
Iannotta, B. and Malik, T. (2009, February 11).
There is a solutionspacecraft operators can plan for the final destination of their old satellites to make sure that any debris falls into a remote area. Defunct satellites are tracked primarily by the United States Air Force, which follows their mass rather than their radio signals.
Instead, Meteosat-7 will begin a complicated series of maneuvers to come to rest in a region at least 125 miles (200 km) above the highest active satellites, according to a statement from the European satellite-monitoring agency EUMETSAT.
For satellites orbiting close to Earth, operators lower the orbit of a decommissioned satellite so that it will naturally re-enter the atmosphere within 25 years (known as the 25-year Rule). Your email address is used only to let the recipient know who sent the email. "It would require the satellite to carry too much propellant it would be too heavy. Other orbital sweet spots, just beyond high Earth orbit, are the Lagrange points. plus another 50 - 100 km for perturbations due to radiation pressure, depending on satellite structure. Built and launched by NASA and operated by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), the GOES satellites provide a search and rescue beacon used to help locate ships and airplanes in distress.
It is the orbit used by the Global Positioning System (GPS) satellites. Republicans are already talking about impeaching her. "You must target, with 90 percent probability, that you will clear this 200 km-plus region," Milan Klinc, a flight dynamics engineer at EUMETSAT, said in the statement. Inclination is the angle of the orbit in relation to Earths equator. The Tropical Rainfall Measuring Mission (TRMM) satellite was launched to monitor rainfall in the tropics. In the early days of space exploration, we didnt worry so much about what would happen to the stuff we launched into orbit. The International Space Station orbits at an inclination of 51.6397 degrees to make it easier for the Space Shuttle and Russian rockets to reach it. "We have allowed a margin for uncertainties and will keep manoeuvring higher up, with up to nine burn manoeuvres.". This method is preferred as it avoids the less predictable re-entry process.
Most satellites in geosynchronous orbits (GEO) have a design life of 15 years and are launched with enough fuel to cover that timeframe.
So, what is the "graveyard orbit," why do we need one and how will Meteosat-7 get there? You can unsubscribe at any time and we'll never share your details to third parties. For many of these high satellites, it takes less fuel to blast it farther into space than to send it back to Earth. It either falls back into Earths atmosphere, only to reach a fiery death as it burns up on atmosphere re-entry. Earlier we looked at geostationary orbits (GEO) . Lagrange Points are the five points where are a small mass can orbit in a constant pattern with two larger objects.
Reviving the spacecraft is a key step in extending the lifetime of orbiting objects; a second mission is set to extend the lifetime of another satellite later this summer. Being the last of the first generation series, this will also mark the end of the 40-year-long history of what was the first European meteorological satellite system in geosynchronous orbit.
We are only in the early, theoretical stages at the moment, but we need to look at a permanent solution involving removing or collecting the old satellites.". MEV-1 is only the beginning. points and significantly reduce the fuel needed to get from one point to another as indicated in the diagram below. Please select the most appropriate category to facilitate processing of your request. Satellites in higher orbits, such as NOAAs Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellites (GOES) orbiting 22,300 miles above the Earth, would require too much fuel to slow down, significantly cutting into their operational life-spans (not to mention the distance they would have to fall! 2018). The satellite orbits in the direction of the Earth's rotation, producing an orbital period equal to the Earth's period of rotation, known as the sidereal day (very nearly 24 hours). Sarah has an MA from NYU's Science, Health and Environmental Reporting Program and an AB in mathematics from Brown University. About 95% of the objects in this illustration are orbital debris, not functional satellites.
In summary, a typical graveyard orbit is about 300 km above GEO, consisting of. googletag.cmd.push(function() { googletag.display('div-gpt-ad-1449240174198-2'); }); After almost 20 years of service a remarkable feat, given its expected lifetime of five years a series of manoeuvres will be carried out to take the satellite out of its current geostationary orbit, 36,000km above the Earth, to its new and final resting place. (2009, February 12). Satellite orbit paradox: A general view. By then, MSG satellites had taken over the 0 service. Both satellites broke apart, creating a field of debris that contained at least 2,500 pieces. Orbital inclination is the angle between the plane of an orbit and the equator. "We have designed it so that after burn number three, we will have cleared the protected region," Klinc said in the statement.
Once the satellite has reached a safe distance from the geostationary protected region, preventive measures will be taken to minimise the potential for the satellite to break up in the future.
The website provides a spreadsheet containing details of all the satellites, which can be downloaded.
These best practices clearly set aspirational targets to encourage all space actors to advance towards a safer, more responsible and sustainable use of space, Charles Law, senior manager of flight dynamics at SES, a telecommunication satellite company, said in the statement.
If a satellite orbits from the north pole (geographic, not magnetic) to the south pole, its inclination is 90 degrees. At the same time as it is being re-orbited, the satellite will be reducing its spin rate, by carefully selecting which thruster to use in the orbital manoeuvres. More Heavy Rain, Snow, and Wind Hitting Western U.S. NASA Selects L3Harris to Develop NOAA GeoXO Imager. The semi-synchronous orbit is a near-circular orbit (low eccentricity) 26,560 kilometers from the center of the Earth (about 20,200 kilometers above the surface).
Anything placed at these points will feel equally pulled toward the Earth and the Sun and will revolve with the Earth around the Sun. The Molniya orbit is highly eccentric: the satellite moves in an extreme ellipse with the Earth close to one edge. In February, MEV-1 successfully brought a zombiesatellite back from the graveyard back into geostationary orbit, where it now serves over 30 customers. When a satellite reaches exactly 42,164 kilometers from the center of the Earth (about 36,000 kilometers from Earths surface), it enters a sort of sweet spot in which its orbit matches Earths rotation. The MEV-1 was designed for interfacing with single-use satellites like the zombie satellite. As satellites get closer to Earth, the pull of gravity gets stronger, and the satellite moves more quickly. Meteosat-8 satellite's new position of 41.5E provides weather and climate view over the Indian Ocean, Humans hunted giant snails on the way to becoming an apex predator, suggests study, Testing of smartphone apps that identify plants shows most are not very good, Viking Age ceremonial burial shields found to be combat ready, Astronomers discover a warm Jupiter-sized exoplanet, Using quantum fluctuations to generate random numbers faster, Science X Daily and the Weekly Email Newsletter are free features that allow you to receive your favorite sci-tech news updates in your email inbox. Details of the orbit. Initially, this solution was reached by agreement between various space agencies.
The company is also developing Mission Extension Pods, smaller propulsion augmentation devices installed on a client's satellite to provide orbital boosts, extending missions for up to six years. The final maneuver occurred in August 2013, after 3,788 days in service. A version of this post appears in the August 2020 print issue as , Inter-Agency Space Debris Coordination Committee, Giving Geostationary Satellites Longer Lives , Survey Shows Overwhelming Interest in a Four-Day Workweek, Using Nuclear Energy to Produce Synthetic Fuels, CubeSat Operators Launch an IoT Space Race, Electronic Warfare, Hackable 5G Networks, and Cell Towers on the Moon.
As far as you and I Orbit is increasingly becoming a busy highway, with more companies launching hoards of satellites above our skies. points have been proposed as good locations for fuel depots and space stations that would serve as stopping points for deep space missions to Mars and elsewhere. part may be reproduced without the written permission. So is that the end of it for these far-away satellites? So object placed there will stay indefinitely. Earth Sun Lagrange Points with contours (Credit: ESA). NASAs low Earth orbit satellites adjust their inclination every year or two to maintain a Sun-synchronous orbit.
Once a satellite is in orbit, it usually takes some work to keep it there. WebFor satellites in geostationary orbit and geosynchronous orbits, the graveyard orbit is a few hundred kilometers beyond the operational orbit. This change will push the satellite into a lower orbit, which will increase its forward velocity.
In September 2022, the FCC issued an order that would require satellites to reenter Earths atmosphere just five years after their missions end, rather than the current 25-year deadline.
Meteosat-7 is a spinning satellite, revolving 100 times per minute.